O heliocentrism is an astronomical theory that defends the centrality of the Sun in the Universe. With that, all the planets and other celestial bodies revolve around it. Although the heliocentric theory was worked on in antiquity, it was from the 16th century onwards, with the model proposed by Nicolaus Copernicus, and, later, with the findings made by Galileo Galilei, that it gained strength in the scientific community, although it was not immediately accepted by the religious context of era.
Read too: Myths and Truths about the Landing of Man on the Moon
Abstract about heliocentrism
It is an astronomical model that argues that the Sun is at the center of the Universe and that the Earth and other celestial bodies orbit it.
It originated in antiquity, but was systematized by Nicolaus Copernicus in the 16th century.
As the model contrasted with the geocentrism and the religious beliefs in vogue, was not immediately accepted.
It was proven by Galileo Galilei and perfected by contemporary and later scientists.
What does heliocentrism say?
The cosmological model of heliocentrism says that the sun is located at the center of the universe and that all the planets revolve around it, including the Earth, the stars and other celestial bodies. In this way, the heliocentrism that established that the Earth describes a circular motion around the Sun, and not the other way around.
The term heliocentrism is formed by two Greek words: helios = sun and kentron = center.
The heliocentric theory revolutionized the Theastronomy, and the technical improvement of the instruments used for the studies of the heavens and the Universe allowed the verification that the planets of the solar system, in fact, revolve around the Sun.
Origin of heliocentrism
The theory of heliocentrism emerged as a counterpoint to the prevailing model until then, Ogeocentrism. The first to theorize about the Universe were the Greek thinkers, still during the fifth century of the Common Era, although their propositions did not have the strength to supplant the geocentric model.
After more than a thousand years with geocentrism as the most accepted theory, Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543) systematized, in the 16th century, a new model that revolutionized the way of thinking in astronomy and challenged the idea that the Earth was the center of the universe. Universe.
This movement became known as Copernican Revolution, and other astronomers and mathematicians made important contributions to his work, which led to the strengthening ofO heliocentryism. In addition to Copernicus, the discoveries of the italian astronomer Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) were fundamental to prove the heliocentric theory.
When was heliocentrism accepted?
The heliocentrism was not immediately accepted by the scientific community, having also suffered resistance from the Catholic Church, which was based on geocentrism to explain the Universe.
The main case of resistance by religious groups concerns Galileo Galilei, considered a heretic by the Court of the Holy Inquisition for his defense of the heliocentric model of Nicolaus Copernicus. The publication of the work Dialogue on the Two Greatest World Systems, in 1632, had Galileo put on trial and condemned by the Inquisition. The astronomer had to publicly deny his discoveries and his defense of the heliocentric theory, and he lived under house arrest until his death in 1642.
Many years passed before the advancement of scientific knowledge allowed greater acceptance of heliocentrism. In the case of the Catholic Church, acceptance of Galileo's evidence takes placeu only in the 19th century. Pardon to the astronomer was only granted in 1992 by Pope John Paul II.
What are the differences between heliocentrism and geocentrism?
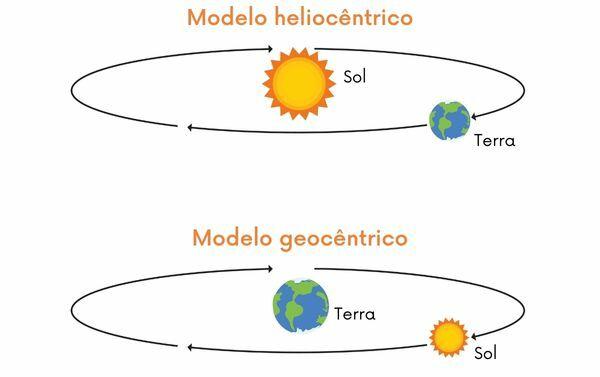
As we have seen so far, the heliocentric theory emerged in opposition to the geocentric theory, accepted to explain the order of the Universe for 1500 years. Understand the differences between them:
Geocentrism: argues that the planet Earth is at the center of the Universe, and the other bodies and stars revolve around it, including the Sun. The planets and the Sun are positioned in concentric spheres, and the sphere farthest from Earth houses the other stars and limits the existing Universe. It was the most accepted theory until the 16th century, with the support of the Catholic Church for postulating ideas similar to those present in the Bible.
Heliocentrism: argues that the Sun is at the center of the Universe, and the Earth and other celestial bodies orbit it. The improvement of astronomical equipment allowed the verification of the movement of the planets around the Sun and the verification that it is in the center of the Solar System. Despite some modifications that were necessary in the theory, heliocentrism is fundamental for the understanding of the Universe, having revolutionized astronomy.
Know more: What if the Earth stopped spinning?
Who was Nicolaus Copernicus?

Nicolas Copernicus (1473-1543) was a Polish astronomer, mathematician and physician. He revolutionized modern science and, more specifically, astronomy by making the systematizationdthe theory of heliocentrism and claim that the Sun is at the center of the Universe and that the Earth revolves around it. That movement of the planet around the Sun assists in explaining phenomena, such as the alternation of seasons.
The book with Copernicus's heliocentric theory was completed in 1530 and was named after Of the revolutions of the celestial spheres. The work, however, was published more than a decade later, in the year of his death. Although he was the author of other publications, the last work was the most important of his life and responsible for what became known as the Copernican Revolution. He left a very important legacy for the Theastronomy, and his postulates served as the basis for future discoveries, like those of Galileo Galilei.
Solved exercises on heliocentrism
question 1
(UFPR) In 1632, the Italian mathematician, astronomer and philosopher Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) published the Dialogue on the two main systems of the world, in which three characters, named Sagredo, Salviati and Simplício, debate Copernican cosmology and Aristotelian cosmology. In the same year, Galileo was summoned to appear before the Congregation of the Holy Office, in Rome, accused of defending the ideas of Copernicus, considered heretical by the Church.
Considering the historical context of the process and condemnation of Galileo Galilei by the Inquisition of Rome, mark the correct alternative.
A) The Inquisition banned the books of Nicolaus Copernicus, relating them to the Index Librorum Prohibitorum, for spreading the Protestant heresy.
B) The inquisitors discovered, in the dialogues between the characters of Galileo Galilei's book, passages in defense of magic as a legitimate form of knowledge of the natural world, reason for banning magic book.
C) The trial against Galileo went beyond an admonition, ordering him to abjure the heliocentrist theory defended by Copernicus and not to divulge or teach it.
D) After the Council of Trent, the doctors of the Church tried to establish an attitude of conciliation and dialogue with naturalist philosophers and mathematicians, with the aim of controlling knowledge of nature.
E) Galileo Galilei's book was a reason for scandal and condemnation, for submitting theology to natural philosophy, questioning religious dogmas and the truth revealed by the Scriptures.
Resolution:
Alternative C
At his condemnation, Galileo Galilei was forced to publicly deny Copernicus' heliocentric theory. The Vatican recognized heliocentrism centuries later, and Galileo's pardon was granted in 1992, 350 years after his death.
question 2
Heliocentrism says that the Sun is at the center of the Universe. By contesting religious teachings, the theory defended by Nicolaus Copernicus and Galileo Galilei was not immediately accepted and suffered great resistance. At the time, heliocentrism contradicted the prevailing model, known as:
A) theocentrism
B) geocentrism
C) anthropocentrism
D) evolutionism
E) creationism
Resolution:
Alternative B
Geocentrism was the most accepted theory to explain the order of the Universe, with the Earth occupying the central position and the other stars orbiting it.
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography Teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/heliocentrismo.htm
